Human Factors and Ergonomics (SIT22008)
3-1. Cognitive Ergonomics I: Information Processing Model
The information processing model (IPM) explains a lot of things related to how we live, including how we think, how we chose and decide, how we learn something, how we feel, how we move, and so forth. As information processing is happening in the human brain, it is related to cognitive work.
The scope of Cognitive Ergonomics is: (1) understanding of how human cognitively behave, (2) improvement of cognitive skills and human performances, and (3) ergonomic/human-centered design for reducing human mistakes as well as decreasing hazardous results can be caused by the human error.
The IPM is one of the basic understandings about human. Students need to be available to explaining human behaviors based on the IPM.
Keywords: #information processing model, #information processing theory, #cognitive process model, #human information processing, #sensory memory, #short-term memory, #working memory, #long-term memory, #attention, #rehearsal
[Video Lectures]
A. Cognitive Ergonomics & Cognitive Engineering/Science
- Human factors and related academic domains
- Human factors in NASA
- Cognitive ergonomics & medical research example
- Cognitive science
-
NOTE. Human factors, cognitive engineering, and cognitive science are not the same academic domains, but there are some common understanding and shared knowledge among those fields.
-
other videos/materials
B. Human Brain
- Human Brain
- How the brain works
C. Information Processing Model (IPM)
- Introduction to IPM
- Other videos of explaining the IPM
- IPM 1: Sensation and perception I
- IPM 1: Sensation and perception II
-
IPM 1: Limiataion of our brain & perception and attention
- IPM 2: Attention - Selective attention
- IPM 2: Attention - Divided attention
- IPM 2: Attention - Multi-tasking
- IPM 3: Memory - Short-term memory
- IPM 3: Memory - Long-term memory
-
IPM 3: Memory - Sensory, working, and long term memory (by Khan Academy)
-
IPM 3: Memory - Movie, Inside Out
- other videos/materials
- Watching the following videos helps for your understaning about attention
- Selective attention test
- Selective attention test
- Divided attention training
- Divided attention example: a card game, “SET”
- Summary of IPM
- Type of memories
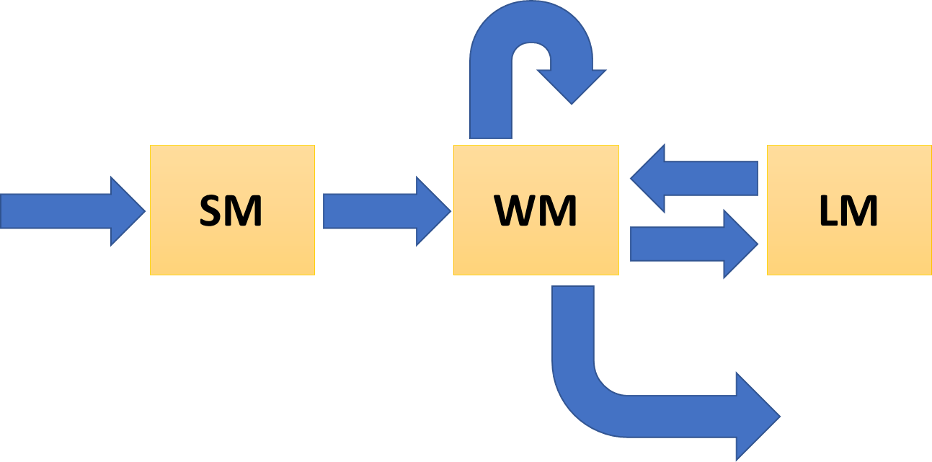
- sensory memory (SM): Human daily perceives a huge amount of information through 5 senses. But most of that information is quickly forgotten unless it is not attended.
- working memory (WM): Also called short-term memory. Any information transferred from SM by the attention is processed for particular purposes such as calculation, comparison, estimation, creation, conceptualization, memorization, and so forth.
- long-term memory (LM): Any treated information is saved/stored in LM if necessary to memorize. Any unsaved information is forgotten even it is once processed in WM.
- Key processes
- Perception
- Attention: Transferring information from SM to WM (selective & divided attention)
- Rehearsal: Repeated handling/treatment of attended information in order to prevent the quick disappearing of information from WM
- Encoding: Saving information from WM to LM
- Recall/Retrieval: Bringing stored information out from LM to WM
- Reaction: Response of human behavior based on the results of the processed information
- Link to human-centered design: A good design makes people’s information processing quick and smooth. But a bad design such as unfamiliar interfaces, hard-to-use controllers, too many texts, unorganized data, complexity, incomplete functions will let people think a lot when they use it. ‘Requiring a lot of thinking’ means that any information is stuck in WM because it is uneasy to be treated in WM.
- Type of memories

D. Sleep and Cognitive Health
I know students are very busy, and resting and sleeping are quite limited during the semester. I cannot easily request you to sleep more, but I want you to know that enough sleep makes the information processing quicker and smoother. Yes, as mentioned above, the IPM can explain every action that human does.
- Lack-of-sleep problem
- Science of sleep
- Measurement of biosignals while sleeping
E. (Optional) Power of Brain
- 타고난 한계를 뛰어넘는 인간은 어떻게 만들어지는가?
Assignments
- Find related essay assignment from Here.
- NOTE. The assignment topic might be changed during the semester but not updated in this site. Please always check LMS.handong.edu.
List of Video Lectures
- 1. Introduction to HF/E
- 2-1. Physical Ergonomics I: Biomechanics
- 2-2. Physical Ergonomics II: Anthropometry, ergonomics at workplace, virtual ergonomics
- 3-1. Cognitive Ergonomics I: Information Processing Model
- 3-2. Cognitive Ergonomics II: Human error, cognitive training, and fight or flight response
- 4-1. Emotional Ergonomics I: Emotional Engineering, Measurement of Human Emotion
- 4-2. Emotional Ergonomics II: Emotional Design
- 5-1. Usability I: Design with Users & Usability Evaluation
- 5-2. Usability II: User-Centered Design Principles